Smart communities will enrich the lives of residents and make local governments more efficient in responding to their citizens’ needs. From security to convenience to revenue generation, Smart City applications will change the way cities operate and the way we live and work, says Ehab Kanary, Vice President of Enterprise, Middle East and Africa, CommScope expert.
It all starts with connectivity – Smart City residents, vehicles, systems and applications must be connected, and in most cases that involves fibre infrastructure.
According to a recent report by KPMG, the amount spent on Smart Cities on technology is set to double in the coming four years within the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region. The total spending is anticipated to increase from $1.3 billion (Dh 4,771 billion) to $2.7 billion (Dh 9,909 billion) during the review period.
Having said that, there are three key trends that will impact Smart Cities in the Middle East in 2019. Let’s take a look.
Longer-term planning
Companies have traditionally built out specific, siloed applications like surveillance cameras, smart lighting or traffic sensors, but for 2019 they will start to take the longer view and think about building a basic infrastructure to support all Smart City applications.
It only makes sense; otherwise, the city is digging up the same streets every year or so to add infrastructure for each new application. For example, one city installed basic security cameras on light poles but did so without installing fibre connectivity that would enable adding small cells to those poles or implementing facial recognition applications for the cameras. Now, the city must upgrade its light pole connectivity network – a painful and costly process.
To avoid having to upgrade networks in the future, city planners are now educating themselves about future possibilities, consulting with IoT vendors and network connectivity vendors, and working to develop a plan for the long term.
Under the Dubai Plan 2021, the government will offer ubiquitous Internet connectivity through high-speed fibre optic and high bandwidth Wi-Fi networks, with 5,000 newly deployed Wi-Fi hotspots providing free Internet connection to 50 billion devices expected to be connected all over the city.
Overall, data connectivity is becoming the Fourth Utility in cities – it’s a must-have to do business, and cities are recognising this. Connectivity in homes and businesses is a competitive advantage for cities, and they are rushing to implement it.
Creative financing
Like water, gas and electricity, cities don’t always deliver the service, but they enable construction of the basic infrastructure that delivers the service. We’re starting to see more projects that combine government funding with public/private partnerships.
In Europe and elsewhere around the world, many national governments are mandating and providing funding for large fibre build-outs. In North America, service providers, developers and local utilities are deploying parts of the civic connectivity infrastructure while the city facilitates permitting and planning for construction.
Electric utilities are in a unique position to deploy fibre infrastructure because they already own rights-of-way and have existing overhead poles or underground conduits that can accommodate new fibre, so they can deploy fibre more quickly and at a lower cost.
In some cases, cities in North America are funding or partnering with local power companies to build out the ‘Middle Mile’ of the fibre network (Figure 1) – the part from central offices or other distribution hubs to neighbourhoods or business parks.
Middle-Mile networks are the most common municipal model due to less risk, the decreased cost of deployment and the ability to lease excess conduit/fibre to private providers. Cities and municipal organisations building Middle-Mile networks include Centennial, Colorado and Howard County, Maryland to name just a few.
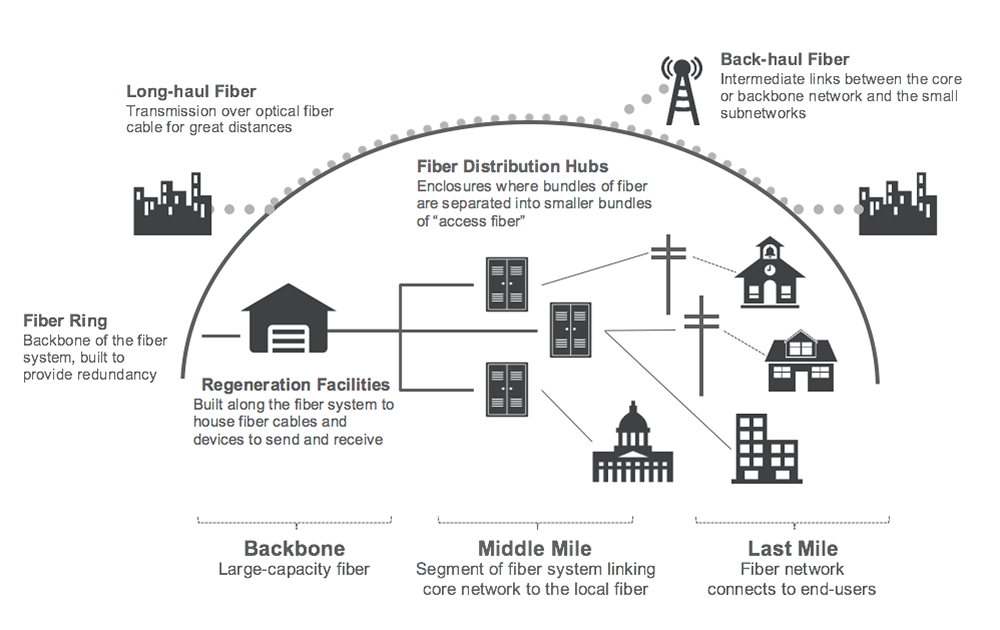
In many other cases, cities are also building the ‘Last Mile’ that connects customers, often in partnership with local municipal electric companies. Ammon, Idaho; Hudson Oaks, Texas; and Fairlawn, Ohio; and are deploying last mile connectivity on their own, while Chattanooga, Tennessee; Lafayette, Louisiana; and Longmont, Colorado are partnering with local electric utilities to reach end customers.
We see similar trends internationally in Stockholm (Stokab), Netherlands (Reggefibre, Citynet Amsterdam) and Singapore (OpenNet) to just name a few. Carriers are also building their own Last-Mile networks, and 5G access will play an increasing role in delivering this connectivity, either through the densification of mobile networks or deployment of new fixed access solutions. Verizon has already launched 5G wireless access trials in several cities in 2018.
Network convergence
In the past, service providers built separate wireless and wireline networks. Wireless infrastructure is becoming more centralised, so it makes more sense to converge all the wireless backhaul traffic onto the same fibre used by wireline services.
The process of fibre network convergence is primarily driven by the development of enabling technologies, user demand and service providers’ capabilities. Large incumbent service providers have both wireline and wireless operations, so converging onto a single network and maximising asset utilisation makes excellent business sense and will be a push for 2019.
Real-life examples have occurred where a fibre-to-the-home (FTTH) network was built and several months later, the same construction crew dug up the same street to lay fibre for a cell site, which is wasteful and disruptive. Network convergence would mean one build-out that could be used for multiple service delivery platforms including FTTH (Figure 1).
That said, most cities will incorporate different providers’ networks in their overall infrastructure. How should they tie all these networks together? The first step is to put all this fibre from different vendors in the same trench and in the same conduit.
Some networks need to be private (public safety, for example), but cities can at least ensure that all networks use the same conduit and perhaps even the same fibre bundle. After all, when the US Interstate Highway system was built, there weren’t separate roads for trucks, cars and motorcycles –a shared infrastructure was built. It makes sense to do the same with fibre networks.
Applications drive the need for more bandwidth: parking, smart meters, public safety (surveillance cameras), traffic management, 5G small cell densification, waste management, and coordination of departments for emergency services are just a few examples.
It’s easy to see that a single converged network would be the most cost-effective way to support these applications. When a city builds out a fibre network to its light poles, for example, those poles can support smart lighting, surveillance cameras and small cells for 5G network densification.
According to GSMA (Groupe Spéciale Mobile Association), 5G will account for 16% of total connections in MENA markets by 2025. In fact, the advent of 5G networks over the next couple of years is a major driver for fibre deployments. 5G will not only bring faster speeds, but also much denser small cell deployments due to distance limitations with millimeter wave technology and ultra-low latency applications at the edge.
By providing the pole infrastructure and facilitating permitting, a city can speed the build-out of fibre-to-the-pole networks by utility companies or service providers.
By meeting these expectations, 5G will foster new applications. Large companies like Netflix and Uber were built because fibre and 4G mobile wireless infrastructure were there to support their services. With its increases in bandwidth and coverage ubiquity, 5G will drive similar innovations, but it will rely on fibre for transport to and from the rest of the city’s network.
Cities are implementing Smart City applications because they improve efficiency, reduce costs, generate new sources of revenue, and most importantly, improve the lives of their citizens. By planning ahead, using creative funding approaches, and converging networks around citywide fibre rollouts, cities will move forward on the path to becoming smarter in 2019.



